基于STM32单片机的太阳能自动跟踪系统设计
1.无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
2.资料以网页介绍的为准,下载后不会有水印.资料仅供学习参考之用.
密 惠 保
基于STM32单片机的太阳能自动跟踪系统设计(论文12000字)
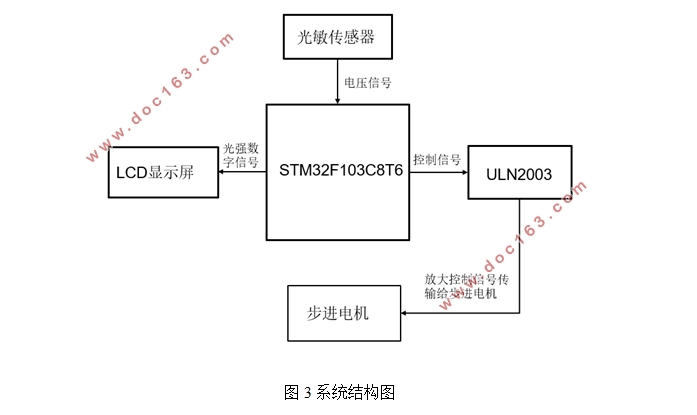
摘要:近些年,新能源汽车的热度不断提升,这一现象一方面反应了人们对能源可持续的担忧,另一方面也反映了人类环境保护意识的增强。面对能源问题,许多人考虑到了太阳能的利用。太阳能可以通过光电转换和光热转换,变成人类所需的电能。这两种形式都对太阳光照的角度有一定的要求。并且由于太阳能发电的成本较高,必须提高其转化效率。因此对太阳照射角度的跟踪系统具有较高的经济价值。本系统利用四个光敏传感器检测太阳光照射角度的变化,并将信号传输给主控STM32F103,由主控驱动双轴步进电机实现自动跟踪。除此之外,还可判断阴天或晴天,调整追踪策略。另外,系统附有LCD显示屏可显示实时光强。
关键字:太阳能;光敏传感器;STM32F103;双轴;自动跟踪
Solar automatic tracking system based on STM32
Abstract:In recent years, the heat of new energy vehicles has been increasing. This phenomenon reflects people's concerns about energy sustainability, and on the other hand, it reflects the awareness of human environmental protection.In the face of energy problems, many people think of the use of solar energy.Solar energy can be converted into electrical energy required by humans through photoelectric conversion and photothermal conversion. Both of these forms have certain requirements for the angle of the sun.And because the cost of solar power generation is high, it is necessary to increase its conversion efficiency. Therefore, the tracking system for the angle of the sun has a high economic value.The system uses four photosensitive sensors to detect the change of the sunlight illumination angle, and transmits the signal to the MCU STM32F103, which is driven by the main control to drive the two-axis stepper motor.In addition, you can judge the cloudy or sunny days and adjust the tracking strategy. In addition, the system is equipped with an LCD screen to display real-time light intensity. [资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
Key words:Solar energy;Photosensitive sensor;STM32F103; Two-axis;Automatic tracking
[资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
目录
1前言 3
2研究现状及原理 3
2.1光伏发电原理 3
2.2太阳自动跟踪系统的目的和意义 4
2.2.1光电追踪 4
2.2.2视日轨迹追踪 5
2.2.3两者结合 5
2.2.4单轴追踪 5
2.2.5双轴追踪 5
2.2.6最终选用方案 6
2.3国内外研究现状 6
3系统设计方案 7
3.1硬件设计 8
3.1.1主控芯片STM32F103C8T6 8
3.1.2电机驱动芯片ULN2003 10
3.1.3 28BYJ-48单极步进电机 12
3.1.4灵敏型光敏传感器 13
3.1.5双轴跟踪结构 14
[版权所有:http://think58.com]
3.1.6 LCD显示屏 14
3.2软件设计 15
3.2.1算法设计 15
3.2.2软件流程 16
4系统调试 17
4.1光源选择 17
4.2测试过程 17
4.3测试总结 18
4.4系统修正 18
4.4.1软件修正 18
4.4.2硬件修正 19
5总结 20
参考文献 21
致谢 22 [资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
