基于51单片机的贪吃蛇游戏设计

1.无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
2.资料以网页介绍的为准,下载后不会有水印.资料仅供学习参考之用.
密 惠 保
基于51单片机的贪吃蛇游戏设计(任务书,开题报告,论文13000字)
摘要
游戏是一种良好的减压方式。贪吃蛇作为一款经典的游戏,自上世纪90年代,诺基亚在手机中内置了这款游戏后,贪吃蛇迅速风靡全球。本次毕设在具体实现上,采用STC89C51单片机作为内核,LCD12864作为显示屏,从而达到贪吃蛇游戏的运行与显示效果,构成一个便捷的游戏机系统。软件实现上,采用C语言,Keil进行软件的调试,Proteus进行电路的设计与仿真,再进行软硬件联调,达到最终的贪吃蛇游戏机成品。本文主要解决了利用51单片机、LCD12864液晶显示屏制作一款益智游戏的问题,贪吃蛇可以通过外部按键控制改变运动方向,玩家可以在菜单界面选择游戏的等级、游戏的地图,游戏中食物的产生是随机的,蛇吃完食物后,蛇身会加长并且游戏的积分会增加,蛇碰撞到蛇身或墙,游戏结束,最终实现了一个基础的游戏机系统。
关键词:贪吃蛇单片机液晶显示屏游戏设计
Design of Snake Game Based On 51 SCM
Abstract
Playing game is a good way to help people reduce stress. Snake Game is a classic game. Since Nokia built this game in its mobile phone in the 1990s, Snake Game has become popular all over the world.In the software implementation, used the C language and Keil was used to debug the software, Proteus was used to design and simulate the circuit, and then the software and hardware were debugged to achieve the final product of Snake Eating Game Machine.This paper mainly solves the problem of making a puzzle game by using 51 single chip computer and LCD 12864 LCD screen. The snake-eater can change the direction of movement by controlling the external keys. Players can choose the difficulty of the game and the map of the game in the menu interface. The production of food in the game is random. After snakes eat food, the body of the snake will lengthen and the score of the game will increase. At the end of the game, players can view their own game results, and ultimately achieve a basic game machine system. [版权所有:http://think58.com]
Key words: Snake Game; Microcontroller ; LCD Display Screen; Game Design
[来源:http://www.think58.com]

目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究的意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状、水平 1
1.3 本课题的发展趋势 2
1.4 本课题的研究内容和达到的要求 2
第二章 方案分析与选择 3
2.1 系统方案设计 3
2.2 显示器模块设计方案 3
2.3 按键输入模块设计方案 4
第三章 系统硬件设计 5
3.1单片机的选择与其性能分析 5 [资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
3.2 键盘电路的设计 6
3.3 液晶屏LCD12864 7
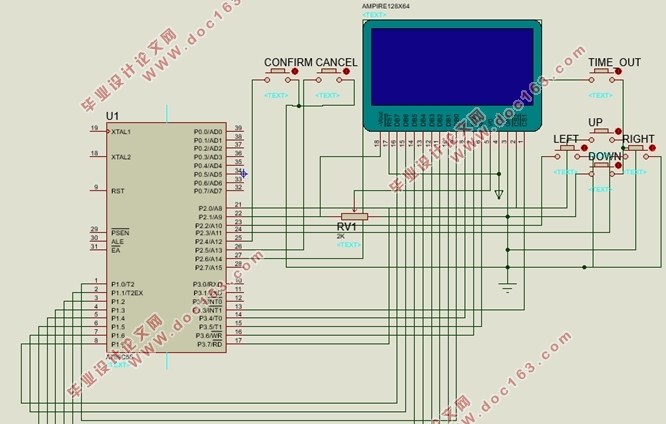
3.4 系统整体硬件设计 12
第四章 软件系统设计 13
4.1 游戏设计思想 13
4.2 主要模块介绍及其功能 14
4.3 程序设计流程图 18
第五章 仿真设计与结果分析 19
5.1 仿真软件的简介 19
5.2 本系统的Proteus仿真设计 20
第六章系统调试 22
6.1 硬件调试 22
6.2 软件调试 23
6.3 硬件软件联合调试 23
6.4 调试结果 24
第七章 总结与展望 25
参考文献 26
致谢 27
附录 28
[资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
