基于FPGA的语音识别到手势图像显示系统设计

1.无需注册登录,支付后按照提示操作即可获取该资料.
2.资料以网页介绍的为准,下载后不会有水印.资料仅供学习参考之用.
密 惠 保
基于FPGA的语音识别到手势图像显示系统设计(任务书,开题报告,论文14000字)
摘 要
据世界卫生组织(WHO)统计,截至2011年世界患有听力障碍的人数达到3.6亿,而随着近年来智能手机的急速普及,以及对日常生活的渗入日益加深,人们对耳机的使用也日渐频繁,患上听力障碍的风险也越来越高。我国作为人口大国,约有1.5亿人患有听力障碍,60岁以上老年人患听力残疾总数超过2000万,是世界上听力障碍人数最多的国家。考虑到多数言语障碍的人能够通过哑语进行基本交流,哑语手势成为主要的交流方式,本课题意图提供一种语音到手势的转换方法,通过语音识别将手势图像显示出来,给语言无障碍者和有障碍者的交流之间提供便捷辅助。当下,许多企业在语音识别技术的研究上投入了大量资金,意图不止在改进原本的算法,而且在新产品上了逐渐脱离键盘控制,转而利用语音命令作为控制信号,这一理念在车载电子系统、消费电子系统、智能家居等方面得到了广泛应用,具有广阔的发展前景。
本设计的主要目标是实现基于FPGA的语音到手势的转换系统。步骤上,首先需要进行孤立词的语音识别训练,以建立孤立词的声学模型,然后根据《中国手语》提供的手势图像拍摄孤立词对应的手势,并转换成二进制文件,最后通过FPGA平台实现孤立词从录制到识别再到输出显示对应手势图像的转换过程。细节上,采用基于隐马尔可夫模型的语音识别原理进行训练建立声学模型,并将训练好的模型同二进制手势图像存储起来作为匹配模板,然后利用硬件描述语言设计系统的基本逻辑单元,并进行软件编程实现系统控制软件核心,进而实现语音到图像中间的一系列转换工作,例如采集、预处理、识别匹配、调用对应结果图形,并且最终显示到液晶屏幕。
关键词:语音到手势转换,FPGA,HMM
Abstract
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of 2011, the number of people with hearing impairment in the world reached 360 million. With the rapid spread of smartphones in recent years and the deepening of daily life, people are increasingly using headphones. Frequently, the risk of hearing impairment is getting higher and higher. As a country with a large population, about 150 million people suffer from hearing impairment. The total number of hearing disabilities in the elderly over 60 years old is more than 20 million. It is the country with the largest number of hearing impairments in the world. Considering that most speech impediments can communicate basicly through dummy language, and mute gestures become the main communication method, this topic intends to provide a speech-to-gesture conversion method, which displays gesture images through speech recognition, and provides language barrier-free and Convenient assistance is provided between the communication of the disabled. Nowadays, many companies have invested a lot of money in the research of speech recognition technology. The intention is not only to improve the original algorithm, but also to gradually remove the keyboard control from the new product and use the voice command as the control signal. Systems, consumer electronics systems, smart homes, etc. have been widely used and have broad prospects for development. [资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
The main goal of this design is to implement an FPGA-based speech-to-gesture conversion system. In the steps, the speech recognition training of isolated words is first needed to establish an acoustic model of isolated words, and then the gesture corresponding to the isolated words is taken according to the gesture image provided by "Chinese Sign Language", and converted into a binary file, and finally isolated by the FPGA platform. The conversion process of the word from the recording to the recognition to the output display corresponding gesture image. In detail, the acoustic recognition model based on the hidden Markov model is used to train the acoustic model, and the trained model and binary gesture image are stored in the SDRAM of the FPGA. Then the Verilog HDL hardware description language is used to design the basic logic of the system. The unit performs the voice-to-image conversion function and performs display on the liquid crystal screen to complete the gesture speech to image conversion.
Keywords: speech to gesture conversion, FPGA, HMM
文章内容分为五章进行,如下:
第1章,简介语音识别技术的发展历史,并且解释了SOPC技术,阐释本次设计的主要工作内容。
第2章,基于HMM的孤立词语音识别原理。此处对比了部分主流的语音识别中的特征提取和模版匹配算法,得出适用于本次设计的最佳算法。
第3章,系统整体设计。本章介绍了系统各个模块的设计,对它们的原理、结构、功能以及实现方式进行了介绍。
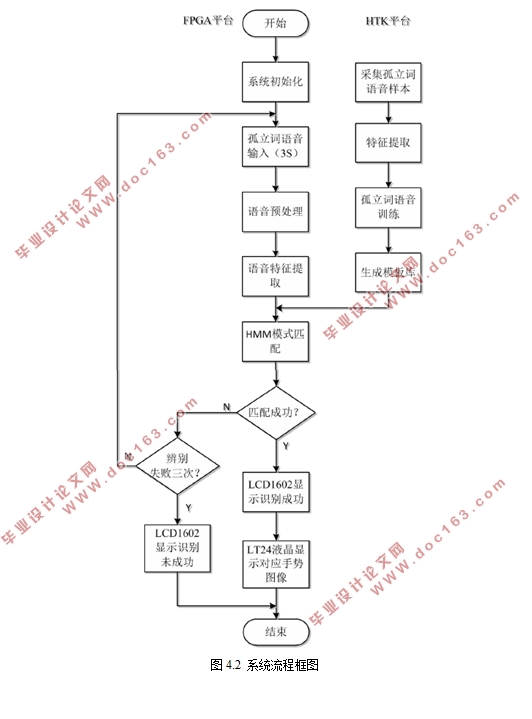
第4章,系统整体实现。本章介绍了系统整体实现的过程,并利用HTK工具箱对软硬件仿真平台进行了识别测试,对系统性能以及测试结果进行了分析和总结。
第5章,对主要工作进行了总结,指出目前存在的不足,提出了下一步改进之处。
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
目 录 III
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 SOPC 技术 1
1.2.1 SOPC 简介 1
1.2.2 FPGA 简介 2
1.3 主要工作 2
1.4 论文主要内容安排 2
第2章语音识别原理 4
2.1 基本原理 4
2.2 语音信号的特征提取 5
2.2.1 线性预测分析 5
2.2.2 倒谱分析 6
2.3 模版匹配 7
2.3.1 动态时间规整 7
2.3.2 人工神经网络 7
2.3.3 隐马尔可夫模型 8
2.4 基于HMM的训练和识别算法 8
2.4.1 Baum-Welch 算法 8
2.4.2 Viterbi算法 10
2.5 HTK 工具箱 10
2.5.1 HTK 软件结构 11
2.5.2 孤立词训练和识别 11
2.6 本章小结 13
第3章系统整体设计 15
3.1 FPGA设计基础 15
3.1.1 FPGA 简介及开发流程 15
3.1.2 FPGA 硬件开发板简介 17
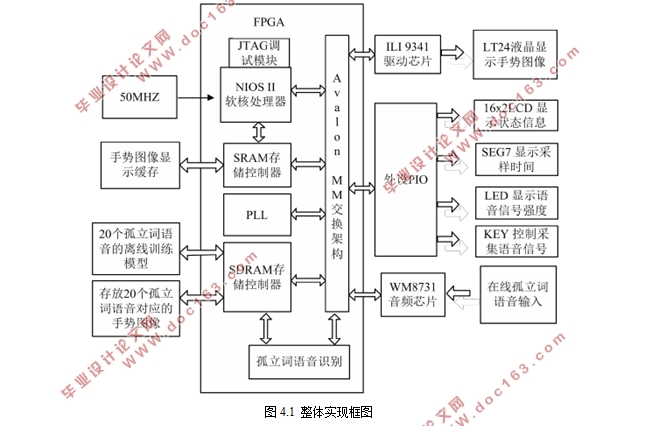
3.2 系统整体架构设计 18
3.3 FPGA中各功能模块的设计 19
3.3.1 语音采集模块 19
3.3.2 存储系统设计 21
3.3.3 NIOS II 程序控制模块 22
[资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
3.3.4 液晶显示模块 25
3.4 本章小结 26
第4章系统整体实现 27
4.1 系统整体框图 27
4.2 性能分析 28
4.2.1 系统资源利用 28
4.2.2 系统运行速度 29
4.3 系统功能测试 31
4.4 本章小结 33
第5章 总结 34
参考文献 35
致 谢 38 [资料来源:http://www.THINK58.com]
